Page 107 - 《广西植物》2022年第10期
P. 107
10 期 廖苗等: 基于分子证据确认秦岭藤属与驼峰藤属(夹竹桃科)的系统位置 1 7 2 5
分支节点数据代表 SH ̄aLRT 和 UFboot 2 个支持率ꎬSH ̄aLRT≥80% 且 UFboot≥95%ꎬ视为结果可信ꎬ分支的划分参照 Liede ̄
Schumann 等(2016)ꎮ 下同ꎮ
Each branch assigned with SH ̄aLRT and UFboot supportsꎬ if SH ̄aLRT≥80% and UFboot≥95%ꎬ the result is considered to be credibleꎬ clade
designations follow those of Liede ̄Schumann et al. (2016). The same below.
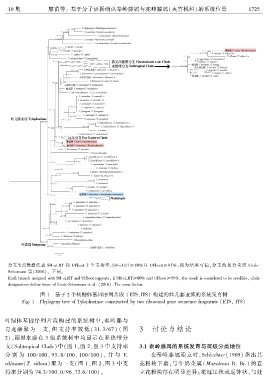
图 1 基于 2 个核糖体基因序列片段 (ETS、ITS) 构建的娃儿藤亚族的系统发育树
Fig. 1 Phylogeny tree of Tylophorinae constructed by two ribosomal gene sequence fragments (ETSꎬ ITS)
叶绿体基因序列片段构建的系统树中ꎬ秦岭藤与
青龙藤 聚 为 一 支ꎬ 但 支 持 率 较 低 ( 31. 3 / 67) ( 图 3 讨论与结论
2)ꎬ而黑水藤在 3 组系统树中均显示在亚热带分
支(Subtropical Clade)中(图 1、图 2、图 3 中支持率 3.1 秦岭藤属的系统发育与属级分类地位
分 别 为 100 / 100、 93. 8 / 100、 100 / 100 )ꎬ 并 与 V. 在秦岭藤属建立时ꎬSchlechter(1905) 指出其
villosum(T. villosa)聚为一支( 图 1、图 2、图 3 中支 花粉块下垂ꎬ与牛奶菜属( Marsdenia R. Br.) 的直
持率分别为 74.3 / 100、0 / 96、72.6 / 100)ꎮ 立花粉块存在明显差异ꎻ花冠坛状或近钟状ꎬ与娃