Page 54 - 《广西植物》2024年第7期
P. 54
1 2 5 4 广 西 植 物 44 卷
关性ꎬ其中 TN 是驱动团聚体稳定性变异的最关键
因子ꎮ
参考文献:
AKSAKAL ELꎬ ANGIN Lꎬ SARI Sꎬ 2020. A new approach for
calculating aggregate stability: mean weight aggregate
stability (MWAS) [J]. Catenaꎬ 194: 104708.
BAO SDꎬ 2000. Soil agrochemical analysis [M]. Beijing: China
Agriculture Press: 1-120. [鲍士旦ꎬ 2000. 土壤农化分析
[M]. 北京: 中国农业出版社: 1-120.]
BAVEL CHMVꎬ 1950. Mean weight ̄diameter of soil aggregates
as a statistical index of aggregation 1 [J]. Soil Sci Soc Am
Jꎬ 14: 20-23.
BESALATPOUR AAꎬ AYOUBI Sꎬ HAJABBASI MAꎬ et al.ꎬ
2013. Estimating wet soil aggregate stability from easily
available properties in a highly mountainous watershed
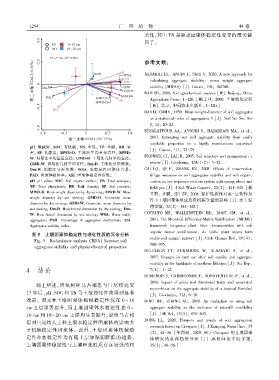
pH. 酸碱度ꎻ SOC. 有机碳ꎻ TN. 全氮ꎻ TP. 全磷ꎻ BD. 容
[J]. Catenaꎬ 111: 72-79.
重ꎻ SP. 孔隙度ꎻ MWD ̄D. 干筛法平均重量直径ꎻ MWD ̄
BRONICK CJꎬ LAL Rꎬ 2005. Soil structure and management: a
W. 湿筛法平均重量直径ꎻ GMD ̄D. 干筛法几何平均直径ꎻ
review [J]. Geodermaꎬ 124(1/ 2): 3-22.
GMD ̄W. 湿筛法几何平均直径ꎻ Dm ̄D. 干筛法分形维数ꎻ
Dm ̄W. 湿筛法分形维数ꎻ WSA. 水稳定性团聚体含量ꎻ CAI LQꎬ QI Pꎬ ZHANG RZꎬ 2008. Effects of conservation
PAD. 团聚体破坏率ꎻ ASI. 团聚体稳定性指数ꎮ tillage measures on soil aggregates stability and soil organic
pH. pH valueꎻ SOC. Soil organic carbonꎻ TN. Total nitrogenꎻ carbon in two sequence rotation system with spring wheat and
TP. Total phosphorusꎻ BD. Bulk densityꎻ SP. Soil porosityꎻ field pea [J]. J Soil Water Conservꎬ 22(2): 141-145. [蔡
MWD ̄D. Mean weight diameter by dry sievingꎻ MWD ̄W. Mean 立群ꎬ 齐鹏ꎬ 张仁陟ꎬ 2008. 保护性耕作对麦-豆轮作条
weight diameter by wet sievingꎻ GMD ̄D. Geometric mean
件下土壤团聚体组成及有机碳含量的影响 [J]. 水土保
diameter by dry sievingꎻ GMD ̄W. Geometric mean diameter by
持学报ꎬ 22(2): 141-145.]
wet sievingꎻ Dm ̄D. Mass fractal dimension by dry sievingꎻ Dm ̄
COTRUFO MFꎬ WALLENSTEIN MDꎬ BOOT CMꎬ et al.ꎬ
W. Mass fractal dimension by wet sievingꎻ WSA. Water stable
aggregatesꎻ PAD. Percentage of aggregates destructionꎻ ASI. 2013. The Microbial Efficiency ̄Matrix Stabilization (MEMS)
Aggregates stability index. framework integrates plant litter decomposition with soil
organic matter stabilization: do labile plant inputs form
图 5 土壤团聚体稳定性与理化性质的冗余分析
stable soil organic matter? [J]. Glob Change Biolꎬ 19(4):
Fig. 5 Redundancy analysis (RDA) between soil
988-995.
aggregates stability and physicochemical properties
DELELEGN YTꎬ PURAHONG Wꎬ BLAZEVIC Aꎬ et al.ꎬ
2017. Changes in land use alter soil quality and aggregate
stability in the highlands of northern Ethiopia [J]. Sci Repꎬ
4 结论 7(1): 1-12.
DEMENOIS Jꎬ CARRICONDE Fꎬ BONAVENTURE Pꎬ et al.ꎬ
2018. Impact of plant root functional traits and associated
综上所述ꎬ固氮树种马占相思与巨尾桉混交
mycorrhizas on the aggregate stability of a tropical Ferralsol
17 年后ꎬpH、SOC 和 TN 等土壤理化性质得到显著
[J]. Geodermaꎬ 312: 6-16.
改善ꎮ 混交林土壤团聚体机械稳定性仅在 0 ~ 10 DING WFꎬ ZHANG XCꎬ 2016. An evaluation on using soil
cm 土层显著提升ꎬ而土壤团聚体水稳定性在 0 ~ aggregate stability as the indicator of interrill erodibility
10 cm 和 10 ~ 20 cm 土层均显著提升ꎬ说明马占相 [J]. J Mt Sciꎬ 13(5): 831-843.
思对巨尾桉人工林土壤水稳定性团聚体的影响大 DONG LLꎬ 2020. Hotspots and trends of soil aggregation
research based on Citespace [J]. J Xianyang Norm Univꎬ 35
于机械稳定性团聚体ꎮ 此外ꎬ土壤团聚体机械稳
(2): 48-56. [董莉丽ꎬ 2020. 基于 Citespace 的土壤团聚
定性和水稳定性均有随土层加深而降低的趋势ꎮ 体研 究 热 点 和 趋 势 分 析 [ J]. 咸 阳 师 范 学 院 学 报ꎬ
土壤团聚体稳定性与土壤理化性质存在较强的相 35(2): 48-56.]