Page 93 - 《广西植物》2022年第3期
P. 93
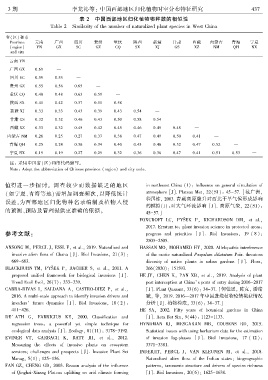
3 期 李龙沁等: 中国西部地区归化植物时空分布特征研究 4 3 7
表 2 中国西部地区归化植物物种数的相似性
Table 2 Similarity of the number of naturalized plant species in West China
省(区)和市
Province 云南 广西 四川 贵州 重庆 陕西 新疆 甘肃 西藏 内蒙古 青海 宁夏
(region) YN GX SC GZ CQ SX XJ GS XZ NM QH NX
and city
云南 YN —
广西 GX 0.69 —
四川 SC 0.59 0.55 —
贵州 GZ 0.55 0.56 0.65 —
重庆 CQ 0.48 0.48 0.63 0.59 —
陕西 SX 0.41 0.42 0.57 0.51 0.58 —
新疆 XJ 0.33 0.33 0.43 0.39 0.43 0.54 —
甘肃 GS 0.32 0.32 0.46 0.43 0.50 0.58 0.54 —
西藏 XZ 0.33 0.32 0.45 0.42 0.45 0.46 0.45 0.48 —
内蒙古 NM 0.26 0.25 0.27 0.37 0.38 0.47 0.49 0.50 0.41 —
青海 QH 0.25 0.24 0.36 0.34 0.40 0.45 0.46 0.52 0.47 0.52 —
宁夏 NX 0.19 0.19 0.27 0.29 0.32 0.36 0.36 0.47 0.41 0.51 0.53 —
注: 采用中国省(区)和市代码缩写ꎮ
Note: Adopt the abbreviation of Chinese province (region) and city code.
值得进一步探讨ꎮ 调查较少而数据缺乏的地区 in northwest China (I): Influence on general circulation of
(如宁夏、青海等地)需增加调查频次ꎬ以降低统计 atmosphere [J]. Plateau Metꎬ 22(S1): 45-57. [范广洲ꎬ
程国栋ꎬ 2003. 青藏高原隆升对西北干旱气候形成影响
误差ꎬ为西部地区归化物种名录编制及植物入侵
的模拟(I):对大气环流影响 [J]. 高原气象ꎬ 22(S1):
的预测、预防及管理提供更准确的依据ꎮ
45-57.]
FOXCROFT LCꎬ PYŠEK Pꎬ RICHARDSON DMꎬ et al.ꎬ
2017. Erratum to: plant invasion science in protected areas:
参考文献: progress and priorities [ J ]. Biol Invasionsꎬ 19 ( 8 ):
2503-2505.
ANSONG Mꎬ PERGL Jꎬ ESSL Fꎬ et al.ꎬ 2019. Naturalized and HASSAN MOꎬ MOHAMED HYꎬ 2020. Allelopathic interference
invasive alien flora of Ghana [J]. Biol Invasionsꎬ 21(3): of the exotic naturalized Paspalum dilatatum Poir. threatens
669-683. diversity of native plants in urban gardens [ J]. Floraꎬ
BLACKBURN TMꎬ PYŠEK Pꎬ BACHER Sꎬ et al.ꎬ 2011. A 266(2020): 151593.
proposed unified framework for biological invasions [ J]. HE JYꎬ CHEN Kꎬ PAN XBꎬ et al.ꎬ 2019. Analysis of plant
Trend Ecol Evolꎬ 26(7): 333-339. pest interception at China’s ports of entry during 2016-2017
CABRA ̄RIVAS Iꎬ SALDANA Aꎬ CASTRO ̄DIEZ Pꎬ et al.ꎬ [J]. Plant Quarantꎬ 33(6): 34-37. [何佳遥ꎬ 陈克ꎬ 潘绪
2016. A multi ̄scale approach to identify invasion drivers and 斌ꎬ 等ꎬ 2019. 2016—2017 年中国进境植物疫情截获情况
invaders’ future dynamics [ J]. Biol Invasionsꎬ 18 ( 2): 分析 [J]. 植物检疫ꎬ 33(6): 34-37.]
411-426. HE SAꎬ 2002. Fifty years of botanical gardens in China
DE′ ATH Gꎬ FABRICIUS KEꎬ 2000. Classification and [J]. Acta Bot Sinꎬ 9(44): 1123-1133.
regression trees: a powerful yet simple technique for HYNDMAN RJꎬ MESGARAN MBꎬ COUSENS RDꎬ 2015.
ecological data analysis [J]. Ecologyꎬ 81(11): 3178-3192. Statistical issues with using herbarium data for the estimation
EVINER VTꎬ GARBACH Kꎬ BATY JHꎬ et al.ꎬ 2012. of invasion lag ̄phases [ J ]. Biol Invasionsꎬ 17 ( 12 ):
Measuring the effects of invasive plants on ecosystem 3371-3381.
services: challenges and prospects [J]. Invasive Plant Sci INDERJITꎬ PERGL Jꎬ VAN KLEUNEN Mꎬ et al.ꎬ 2018.
Managꎬ 5(1): 125-136. Naturalized alien flora of the Indian states: biogeographic
FAN GZꎬ CHENG GDꎬ 2003. Reason analysis of the influence patternsꎬ taxonomic structure and drivers of species richness
of Qinghai ̄Xizang Plateau uplifting on arid climate forming [J]. Biol Invasionsꎬ 20(6): 1625-1638.