Page 94 - 《广西植物》2022年第3期
P. 94
4 3 8 广 西 植 物 42 卷
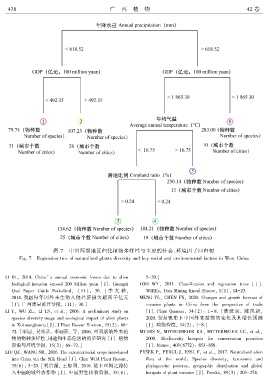
图 7 中国西部地区归化植物多样性与主要的社会、环境因子回归树
Fig. 7 Regression tree of naturalized plants diversity and key social and environmental factors in West China
LI DLꎬ 2014. China’ s annual economic losses due to alien 5-20.]
biological invasion exceed 200 billion yuan [ J]. Guangxi LOH WYꎬ 2011. Classification and regression trees [ J ].
Qual Super Guide Periodicalꎬ ( 11 ): 30. [ 李 大 林ꎬ WIREs: Data Mining Knowl Discovꎬ 1(1): 14-23.
2014. 我国每年因外来生物入侵经济损失超两千亿元 MENG YLꎬ CHEN FXꎬ 2020. Changes and growth forecast of
[J]. 广西质量监督导报ꎬ (11): 30.] invasive plants in China from the perspective of trade
LI Yꎬ WU ZLꎬ LI LSꎬ et al.ꎬ 2006. A preliminary study on [J]. Plant Quarantꎬ 34(2): 1 - 8. [ 蒙 彦 良ꎬ 陈 凤 新ꎬ
species diversity usage and ecological impact of alien plants 2020. 贸易视角下中国外来植物的变化及其增长预测
in Xishuangbanna [J]. J Plant Resour Environꎬ 15(2): 68- [J]. 植物检疫ꎬ 34(2): 1-8.]
72. [李园ꎬ 吴兆录ꎬ 李丽莎ꎬ 等ꎬ 2006. 西双版纳外来植 MYERS Nꎬ MITTERMEIER RAꎬ MITTERMEIER CGꎬ et al.ꎬ
物的物种多样性、用途和生态危害的初步研究 [J]. 植物 2000. Biodiversity hotspots for conservation priorities
资源与环境学报ꎬ 15(2): 68-72.] [J]. Natureꎬ 403(6772): 853-858.
LIU QZꎬ WANG SMꎬ 2016. The extraterritorial crops introduced PYŠEK Pꎬ PERGL Jꎬ ESSL Fꎬ et al.ꎬ 2017. Naturalized alien
into China via the Silk Road [J]. Chin Wild Plant Resourꎬ flora of the world: Species diversityꎬ taxonomic and
35(6): 5-20. [刘启振ꎬ 王思明ꎬ 2016. 陆上丝绸之路传 phylogenetic patternsꎬ geographic distribution and global
入中国的域外农作物 [J]. 中国野生植物资源ꎬ 35(6): hotspots of plant invasion [J]. Presliaꎬ 89(3): 203-274.