Page 177 - 《广西植物》2023年第3期
P. 177
3 期 毛艳娇等: 普定喀斯特次生林木本植物叶生活型比例和谱系多样性的驱动因素 5 7 7
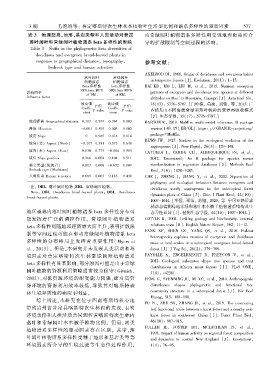
表 3 地理距离、地形、基岩类型和人类活动对普定 而常绿阔叶植物谱系多样性则受到地理距离所介
落叶阔叶和常绿阔叶植物谱系 beta 多样性的影响 导的扩散限制等空间过程的影响ꎮ
Table 3 Shifts in the phylogenetic beta diversities of
deciduous and evergreen broad ̄leaved plants in
response to geographical distanceꎬ topographyꎬ 参考文献:
bedrock type and human activities
AXELROD DIꎬ 1966. Origin of deciduous and evergreen habits
落叶阔叶 常绿阔叶
植物谱系 植物谱系 in temperate forests [J]. Evolutionꎬ 20(1): 1-15.
beta 多样性 beta 多样性 BAI KDꎬ MO Lꎬ LIU Mꎬ et al.ꎬ 2015. Nutrient resorption
SES.beta MPD SES.beta MPD
影响因子 patterns of evergreen and deciduous tree species at different
of DBL of EBL
Influence factor
altitudes on Mao’er Mountainꎬ Guangxi [J]. Acta Ecol Sinꎬ
效应值 效应值 35(17): 5776-5787. [白坤栋ꎬ 莫凌ꎬ 刘铭ꎬ 等ꎬ 2015. 广
P 值 P 值
Coeffi ̄ Coeffi ̄
P value P value 西猫儿山不同海拔常绿和落叶树种的营养再吸收模式
cient cient
[J]. 生态学报ꎬ 35(17): 5776-5787.]
地理距离 Geographical distance 0.103 0.599 0.964 0.003
BARTO ' N Kꎬ 2019. MuMIn: multi ̄model inference. R package
海拔 Elevation -0.001 0.505 0.003 0.102 version 1.43. 15 [EB/ OL]. https: :/ / CRAN.R-project.org/
package=MuMIn.
坡度 Slope 0 0.985 0.014 0.118
BEWS JWꎬ 1927. Studies in the ecological evolution of the
坡向(北) Aspect (North) -0.107 0.381 0.073 0.648
angiosperms [J]. New Phytolꎬ 26(3): 129-148.
坡向(东) Aspect (East) 0.030 0.775 -0.004 0.983
CAYUELA Lꎬ CERDA GLÍꎬ ALBUQUERQUE FSꎬ et al.ꎬ
坡位 Slope position 0.366 0.004 0.104 0.511 2012. Taxonstand: An R package for species names
standardisation in vegetation databases [ J]. Methods Ecol
基岩类型(泥灰岩) 0.813 0.008 -0.672 0.109
Bedrock type (Marlstone) Evolꎬ 3(6): 1078-1083.
人类活动 Human activities 0.689 0.003 0.183 0.430 CHE Jꎬ ZHENG Jꎬ JIANG Yꎬ et al.ꎬ 2020. Separation of
phylogeny and ecological behaviors between evergreen and
注: DBL. 落叶阔叶植物ꎻEBL. 常绿阔叶植物ꎮ
deciduous woody angiosperms in the subtropical forest
Note: DBL. Deciduous broad ̄leaved plantsꎻ DBL. Deciduous
dynamics plots of China [J]. Chin J Plant Ecolꎬ 44(10):
broad ̄leaved plants.
1007-1014. [车俭ꎬ 郑洁ꎬ 蒋娅ꎬ 2020ꎬ 等. 中国亚热带森
林动态监测样地常绿和落叶木本被子植物谱系结构及生
地区森林内落叶阔叶植物谱系 beta 多样性分布可 态习性差异 [J]. 植物生态学报ꎬ 44(10): 1007-1014.]
能发挥着广泛的调控作用ꎮ 常绿阔叶植物谱系 COTTLE Rꎬ 2004. Linking geology and biodiversity. external
beta 多样性则随地理距离增大而上升ꎬ表明扩散限 relations team [R]. English Nature Reportꎬ 562: 11-12.
FANG XFꎬ SHEN GCꎬ YANG QSꎬ et al.ꎬ 2016. Habitat
制等空间过程可能在驱动常绿阔叶植物谱系 beta
heterogeneity explains mosaics of evergreen and deciduous
多样性的分布格局上发挥着重要作用( Myers et
trees at local ̄scales in a subtropical evergreen broad ̄leaved
al.ꎬ 2013)ꎮ 但是ꎬ本研究并未发现人类活动和环 forest [J]. J Veg Sciꎬ 28(2): 379-388.
境因素对普定喀斯特次生林常绿阔叶植物谱系 FAYOLLE Aꎬ ENGELBRECHT Bꎬ FREYCON Vꎬ et al.ꎬ
2012. Geological substrates shape tree species and trait
beta 多样性有显著影响ꎬ部分原因可能是由于常绿
distributions in African moist forests [ J]. PLoS ONEꎬ
阔叶植物的资源利用策略通常较为保守( Givnishꎬ
7(8): e42381.
2002)ꎬ对低资源环境的耐受能力较强ꎬ而对高资 FENG Gꎬ SVENNING JCꎬ MI XCꎬ et al.ꎬ 2014. Anthropogenic
源环境的资源利用效率较低ꎬ导致其对喀斯特森 disturbance shapes phylogenetic and functional tree
community structure in a subtropical forest [ J]. For Ecol
林生境异质性的响应不明显ꎮ
Managꎬ 313: 188-198.
综上所述ꎬ本研究在位于西南喀斯特核心地
FU PLꎬ ZHU SDꎬ ZHANG JLꎬ et al.ꎬ 2019. The contrasting
带的贵州省普定县喀斯特次生林内的发现ꎬ表明 leaf functional traits between a karst forest and a nearby non ̄
环境条件和人类活动共同调控着喀斯特次生林内 karst forest in south ̄west China [ J]. Funct Plant Biolꎬ
落叶和常绿阔叶木本被子植物比例ꎮ 但是ꎬ两类 46(10): 907-915.
FULLER JLꎬ FOSTER DRꎬ MCLACHLAN JSꎬ et al.ꎬ
植物谱系多样性的驱动因素存在区别ꎮ 其中ꎬ落
1998. Impact of human activity on regional forest composition
叶阔叶植物谱系多样性受制于地形和基岩类型等
and dynamics in central New England [ J]. Ecosystemsꎬ
环境因素所介导的生境过滤等生态位过程作用ꎻ 1(1): 76-95.