Page 157 - 《广西植物》2020年第3期
P. 157
3 期 张增可等: 环境因子对海岛植物茎、叶功能性状的影响 4 3 7
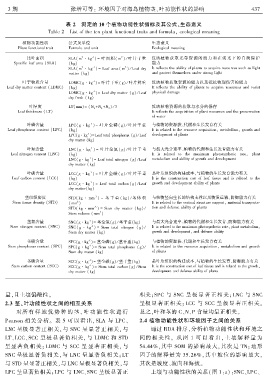
表 2 测定的 10 个植物功能性状指标及其公式、生态意义
Table 2 List of the ten plant functional traits and formulaꎬ ecological meaning
植物功能性状 公式及单位 生态意义
Plant functional trait Formula and unit Ecological meaning
比叶面积 SLA(m kg ) = 叶面积( m ) / 叶片干重 反映植物获取 光等资源 的能力和在 强光下的自 我保护
2
2
 ̄1
Specific leaf area (SLA) (kg) 能力
 ̄1
2
2
SLA(m kg ) = Leaf area( m ) / Leaf dry It reflects the ability of plants to acquire resources such as light
matter (kg) and protect themselves under strong light
叶干物质含量 LDMC(gkg )= 叶片干重( g) / 叶片鲜重 反映植物获取资源的能力以及抵抗物理伤害的能力
 ̄1
Leaf dry matter content (LDMC) (kg) It reflects the ability of plants to acquire resources and resist
 ̄1 physical damage
LDMC(gkg ) = Leaf dry matter ( g) / Leaf
dry fresh (kg)
叶厚度 LT(mm)= (N 1 +N 2 +N 3 ) / 3 反映植物资源的获取与水分的保存
Leaf thickness (LT) It reflects the acquisition of plant resources and the preservation
of water
叶磷含量 LPC( gkg ) = 叶片全磷( g) / 叶片干重 与植物的资源获、代谢和生长发育有关
 ̄1
Leaf phosphorus content (LPC) (kg) It is related to the resource acquisitionꎬ metabolismꎬ growth and
 ̄1
LPC(gkg )= Leaf total phosphorus (g) / Leaf development of plants
dry matter (kg)
叶氮含量 LNC( gkg ) = 叶片全氮( g) / 叶片干重 与最大光合速率、植物的代谢和生长发育能力有关
 ̄1
Leaf nitrogen content (LNC) (kg) It is related to the maximum photosynthetic rateꎬ plant
 ̄1
LNC(gkg )= Leaf total nitrogen (g) / Leaf metabolism and ability of growth and development
dry matter (kg)
叶碳含量 LCC(gkg ) = 叶片全碳( g) / 叶片干重 是叶片组织的构建成本ꎬ与植物的生长发育能力有关
 ̄1
Leaf carbon content (LCC) (kg) It is the construction cost of leaf tissue and is related to the
 ̄1 growth and development ability of plants
LCC(gkg ) = Leaf total carbon ( g) / Leaf
dry matter(kg)
茎组织密度 STD( kg mm ) = 茎 干 重 ( kg) / 茎 体 积 与植物竖向生长的结构支撑以及物质运输、防御能力有关
 ̄3
3
Stem tissue density (STD) (mm ) It is related to the vertical structure supportꎬ material transporta ̄
 ̄3 tion and defense ability of plants
STD( kg mm ) = Stem dry matter ( kg) /
3
Stem volume (mm )
茎氮含量 SNC(gkg )= 茎全氮(g) / 茎干重(kg) 与最大光合速率、植物的代谢和生长发育、防御能力有关
 ̄1
Stem nitrogen content (SNC) SNC( g kg ) = Stem total nitrogen ( g) / It is related to the maximum photosynthetic rateꎬ plant metabolismꎬ
 ̄1
Stem dry matter (kg) growth and developmentꎬ and defense ability
茎磷含量 SPC(gkg )= 茎全磷(g) / 茎干重(kg) 与植物的资源获、代谢和生长发育有关
 ̄1
Stem phosphorus content (SPC) SPC(g kg ) = Stem total phosphorus ( g) / It is related to the resource acquisitionꎬ metabolism and growth
 ̄1
Stem dry matter (kg) of plants
茎碳含量 SCC(gkg )= 茎全碳(g) / 茎干重(kg) 是叶片组织的构建成本ꎬ与植物的生长发育、防御能力有关
 ̄1
 ̄1
Stem carbon content (SCC) SCC(gkg ) = Stem total carbon( g) / Stem It is the construction cost of leaf tissue and is related to the growthꎬ
dry matter (kg) development and defense ability of plants
量ꎬ且土壤偏酸性ꎮ 相关ꎻSPC 与 SNC 呈极显著正相关ꎻLNC 与 SNC
2.3 茎、叶功能性状之间的相互关系 呈极显著正相关ꎻLCC 与 SCC 呈极显著正相关ꎮ
对所 有 样 地 优 势 种 的 茎、 叶 功 能 性 状 进 行 总之ꎬ叶和茎的 C、N、P 含量均呈正相关ꎮ
Pearson 相关分析ꎮ 表 5 可 以 看 出ꎬSLA 与 LPC、 2.4 植物功能性状和环境因子之间的关系
LNC 呈极显著正相关ꎬ与 SNC 呈显著正相关ꎬ与 通过 RDA 排序ꎬ分析植物功能性状和环境之
LT、LCC、SCC 呈极显著负相关ꎬ与 LDMC 和 STD 间的 相 关 性ꎮ 从 图 1 可 以 看 出ꎬ 土 壤 解 释 量 为
呈显著 负 相 关ꎻLDMC 与 SCC 呈 显 著 正 相 关ꎬ 与 54.44%ꎬ其中 SOM 的影响最大ꎬ其次是 TNꎻ地形
SNC 呈极显著负相关ꎬ与 LNC 呈显著负相关ꎻLT 因子的解释量为 35.26%ꎬ其中坡位的影响最大ꎬ
与 STD 呈显著正相关ꎬ与 LNC 呈极显著负相关ꎬ与 其次是坡度、坡向和海拔ꎮ
LPC 呈显著负相关ꎻLPC 与 LNC、SNC 呈极显著正 土壤与功能性状的关系(图 1:a):SNC、LPC、