Page 159 - 《广西植物》2020年第3期
P. 159
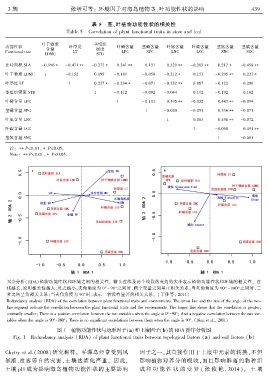
3 期 张增可等: 环境因子对海岛植物茎、叶功能性状的影响 4 3 9
表 5 茎、叶植物功能性状的相关性
Table 5 Correlation of plant functional traits in stem and leaf
叶干物质 茎组织
功能性状 叶厚度 叶磷含量 茎磷含量 叶氮含量 叶碳含量 茎氮含量 茎碳含量
含量 密度
Functional trait LT LPC SPC LNC LCC SNC SCC
LDMC STD
比叶面积 SLA -0.196∗ -0.471∗∗ -0.277∗ 0.281∗∗ 0.131 0.329∗∗ -0.283∗∗ 0.217∗ -0.458∗∗
叶干物质 LDMC 1 -0.152 0.195 -0.189 -0.050 -0.212∗ 0.153 -0.295∗∗ 0.227∗
叶厚度 LT 1 0.227∗ -0.234∗ -0.071 -0.282∗∗ 0.067 -0.122 0.206
茎组织密度 STD 1 -0.112 -0.002 -0.044 0.192 -0.192 0.182
叶磷含量 LPC 1 -0.101 0.395∗∗ -0.032 0.443∗∗ -0.094
茎磷含量 SPC 1 -0.020 -0.051 0.336∗∗ -0.071
叶氮含量 LNC 1 0.083 0.498∗∗ -0.072
叶碳含量 LCC 1 -0.058 0.491∗∗
茎氮含量 SNC 1 -0.081
注: ∗∗P<0.01ꎬ∗ P<0.05ꎮ
Note: ∗∗P<0.01ꎬ∗ P<0.05.
冗余分析(RDA)植物功能性状和环境之间的相关性ꎮ 箭头连线及两个线段的夹角的大小表示植物功能性状和环境的相关性ꎮ 连
线越长ꎬ说明相关性越大ꎬ反之越小ꎻ夹角角度为 0° ~ 90°之间时ꎬ两个变量之间呈正相关关系ꎻ当夹角角度为 90° ~ 180°之间时ꎬ二
者之间呈负相关关系ꎻ当夹角角度为 90°时ꎬ表示二者没有显著的相关关系ꎮ (丁佳等ꎬ 2011)
Redundancy analysis (RDA) of the correlation between plant functional traits and environments. The arrow line and the size of the angle of the two ̄
line segment indicate the correlation between the plant functional traits and the environments. The longer line shows that the correlation is greaterꎬ
contrarily smallerꎻ There is a positive correlation between the two variables when the angle is 0°-90°ꎻ And a negative correlation between the two var ̄
iables when the angle is 90°-180°ꎻ There is no significant correlations between them when the angle is 90°. (Ding et al.ꎬ 2011)
图 1 植物功能性状与地形因子(a)和土壤因子(b)的 RDA 排序分析图
Fig. 1 Redundancy analysis (RDA) of plant functional traits between topological factors (a) and soil factors (b)
Chytry et al.(2008)研究相符ꎮ 平潭岛经常受到风 因子之一ꎬ其直接作用于土壤中元素的转换ꎬ不但
暴潮、盐雾等自然灾害ꎬ土壤盐渍化严重ꎮ 因此ꎬ 影响植物对养分的吸收ꎬ而且影响群落的物种组
土壤 pH 成为影响海岛植物功能性状的主要影响 成和 功 能 性 状 的 变 异 ( 张 俊 艳ꎬ 2014 )ꎮ 土 壤